Penicillin, the ‘wonder drug’ of the 20th century, has saved countless lives since its inception. However, an alarming number of individuals today believe they are allergic to penicillin, often without adequate testing to confirm this condition. Mislabeling penicillin allergy can lead to significant consequences, from prescribing less effective or more toxic antibiotics to increased healthcare costs. But what constitutes accurate penicillin allergy testing, and why is it more important now than ever before? This comprehensive guide will unpack the complexities of penicillin allergies, the gold standards in reliable testing methods, and the overarching impact on patient health and healthcare systems worldwide.
Reliable Testing Methods
The foundation of alleviating these risks begins with reliable testing methods that can accurately diagnose or rule out penicillin allergy.
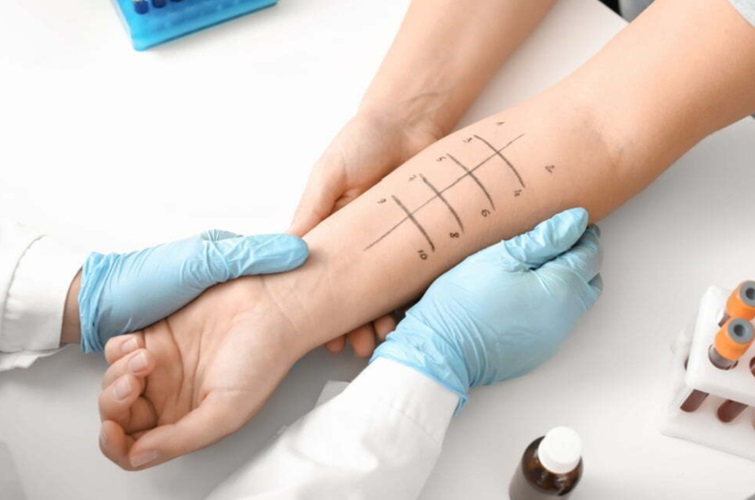
Skin Prick Tests
Skin prick tests are a primary step in diagnosing penicillin allergies, involving the introduction of a tiny amount of penicillin to the skin’s surface. If a reaction, such as a raised bump, occurs, it may indicate an allergy. This method is renowned for its rapid results and high specificity. Nonetheless, a negative result does not conclusively rule out an allergy, necessitating further assessment.
Blood Tests (Specific IgE Testing)
Blood tests, also known as specific IgE testing, measure the level of penicillin-specific antibodies in a patient’s blood. These tests provide valuable information about one’s immune response to penicillin, helping to further clarify allergic sensitivities. Combined with skin prick testing, blood tests can improve diagnostic accuracy and guide appropriate treatment plans.
Oral Challenge Tests
Oral challenge tests are considered the gold standard for penicillin allergy testing. This method involves administering gradually increasing doses of penicillin under close medical supervision. If no adverse reaction occurs, the patient is likely not allergic to penicillin, allowing for broader antibiotic choices in future treatments.
Patch Testing
Patch testing is another pertinent approach for diagnosing delayed allergic reactions to penicillin. Small quantities of penicillin are applied to the skin and covered with a patch for a specific period, usually 48 hours. The skin is then examined for any allergic responses, providing insights into potential delayed hypersensitivity.
Benefits of Accurate Testing
Avoiding Unnecessary Antibiotic Avoidance
One of the most significant benefits of accurate penicillin allergy testing is the avoidance of unnecessary antibiotic avoidance. When patients are incorrectly labelled as penicillin-allergic, healthcare providers are often forced to prescribe alternative antibiotics. These alternatives may not only be less effective but can also contribute to the growing problem of antibiotic resistance, a critical concern for global health systems.
Decreasing Healthcare Costs
Accurate allergy testing plays a vital role in reducing healthcare costs. By ensuring patients can safely receive the most effective antibiotics, healthcare systems can avoid the higher costs associated with more expensive alternative treatments. Using penicillin appropriately reduces hospital stays and lessens reliance on expensive broad-spectrum antibiotics, which can fuel antibiotic resistance.
Improving Patient Outcomes and Treatment Efficacy
Accurate identification of penicillin allergy significantly enhances patient outcomes and ensures the efficacy of treatments. It enables healthcare providers to make informed decisions, utilizing the most effective antibiotic with the least side effects. Consequently, this reduces the risk of adverse drug reactions and promotes faster recovery times, directly benefiting patient health and wellbeing.
Enhancing Awareness and Education
Increasing awareness and education among healthcare professionals and patients about the importance and availability of accurate penicillin allergy testing is crucial. Many individuals may not be aware that their reported allergy could be inaccurately diagnosed, leading to unnecessary caution and suboptimal antibiotic use.
Streamlining Healthcare Protocols
Adopting streamlined protocols that integrate allergy testing into standard patient care can significantly improve the identification and management of true penicillin allergies. By making testing more routine, especially in situations where antibiotic treatment is a likely course of action, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions swiftly.
Challenges and Limitations
Here, we explore the intricacies and hurdles associated with penicillin allergy testing, including potential pitfalls and the barriers to widespread implementation of these necessary tests.
False Positives and Negatives
Despite advancements in diagnostic techniques, the occurrence of false positives and negatives remains a significant challenge. False positives can lead to unnecessary avoidance of penicillin, while false negatives may expose patients to potential allergic reactions.
Access to Specialized Testing Facilities
Access to specialised facilities equipped for allergy testing is not uniformly available globally, creating disparities in healthcare. Patients in remote or under-resourced areas are less likely to undergo these critical tests, perpetuating the cycle of mislabelled allergies and suboptimal antibiotic use.
Patient Compliance and Understanding
Securing patient compliance and understanding poses another hurdle. The process of confirming or ruling out a penicillin allergy requires patient participation in multiple tests, which can be time-consuming and, occasionally, stressful. Healthcare providers must effectively communicate the benefits and necessity of these tests to ensure patients are informed and willing to undergo the process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the path to enhancing clinical outcomes and healthcare efficiency significantly relies on the accurate penicillin allergy testing. The deployment of reliable testing methods, including skin prick, blood, oral challenge, and patch tests, offers a robust framework for diagnosing these allergies with greater precision. Consequently, this not only mitigates the risk associated with unnecessary antibiotic avoidance but also plays a critical role in combating the burgeoning issue of antibiotic resistance. Accurate testing is crucial for reducing healthcare costs and improving patient care by guiding treatment decisions. Addressing challenges like access to facilities, potential false results, and patient compliance is key to maximising the potential of these diagnostic approaches. By increasing awareness, education, and integrating tests into care protocols, the aim of more personalised and effective healthcare can be reached.